ARP Spoofing Mitigation Research
Introduction
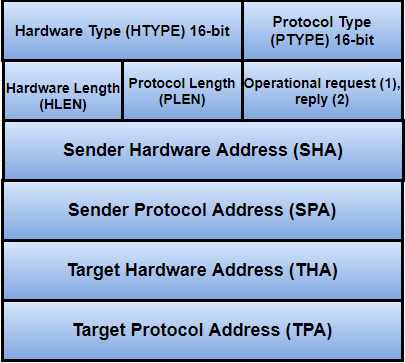
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a fundamental component of Local Area Networks (LANs), mapping IP addresses to MAC addresses. However, ARP lacks built-in security mechanisms, making it vulnerable to spoofing attacks, where an attacker associates their MAC address with a legitimate IP address to intercept or manipulate communication. This research investigates an encryption-based mitigation approach using cryptographic techniques such as HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) and SipHash to secure ARP requests and replies while maintaining efficiency.
Design
Traditional ARP spoofing mitigation techniques, such as static ARP tables and intrusion detection systems, often suffer from scalability and performance issues. Cryptographic solutions like AES and RSA have been proposed in the past but introduce significant processing overhead. This research explores the use of lightweight cryptographic techniques that ensure the authenticity of ARP messages without requiring extensive protocol modifications.
A controlled lab environment was set up using Oracle VirtualBox with Ubuntu 20.04 and Docker containers to simulate an ARP spoofing attack. Three hosts were configured:
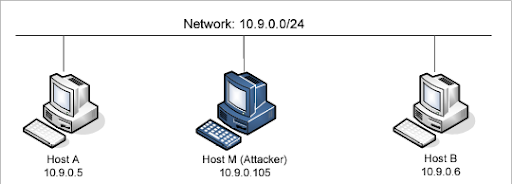
- Host A (10.9.0.5): Legitimate sender
- Host B (10.9.0.6): Intended recipient
- Host M (10.9.0.105): Attacker attempting ARP spoofing
Testing involved baseline spoofing attacks, implementing cryptographic protection, and monitoring network traffic using Wireshark to verify the effectiveness of the mitigation techniques.
My goal
My goals included:
- Researching ARP spoofing techniques and mitigation strategies.
- Implementing HMAC and SipHash-based authentication for ARP messages.
- Designing and conducting controlled network experiments.
- Analyzing results to determine the impact of encryption on network latency and security.
Results & Conclusion
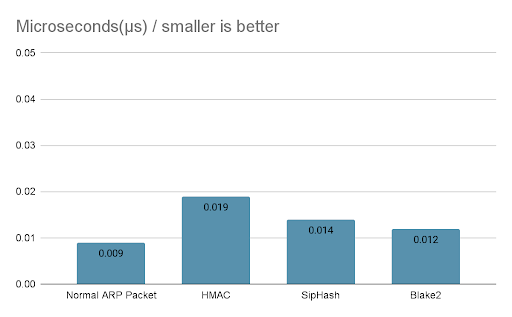
Testing revealed that implementing HMAC and SipHash effectively prevented ARP spoofing attacks by ensuring that only legitimate devices could respond to ARP requests. The round-trip time (RTT) for ARP resolution increased slightly but remained within acceptable limits for real-time network communication.
Pros:
- Enhanced security by preventing unauthorized ARP replies.
- Minimal performance impact compared to heavier cryptographic approaches.
- Compatibility with existing network infrastructure without requiring major modifications.
Cons:
- Increased computational overhead, though manageable.
- Requires key management for shared secrets.
- Non-standard implementation, making widespread adoption challenging.
While cryptographic authentication improves ARP security, practical deployment remains limited due to standardization concerns. Alternative security measures, such as dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) and VLAN segmentation, may provide more scalable solutions for enterprise networks.
This research contributes to the ongoing efforts in cybersecurity by proposing an efficient approach to mitigating ARP spoofing while maintaining network performance.
References
- Address Resolution Protocol. (n.d.). Wireshark Wiki. https://wiki.wireshark.org/AddressResolutionProtocol
- Scapy documentation. (n.d.). https://scapy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
- Hong, S. et al. (2013). Design and implementation of an efficient defense mechanism against ARP spoofing attacks using AES and RSA. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 58(1–2), 254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2012.08.008
- CertBros. (n.d.). [Video]. YouTube. Retrieved September 13, 2024, from https://youtu.be/A7nih6SANYs
- Full Write Up: Source